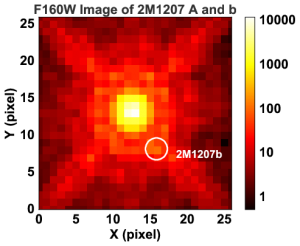
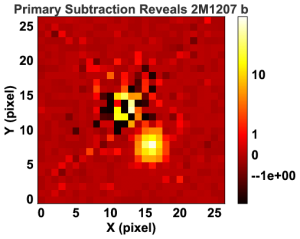
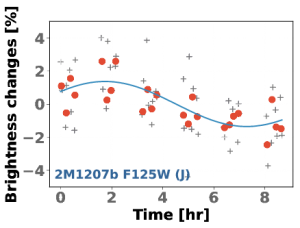
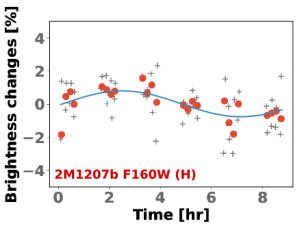
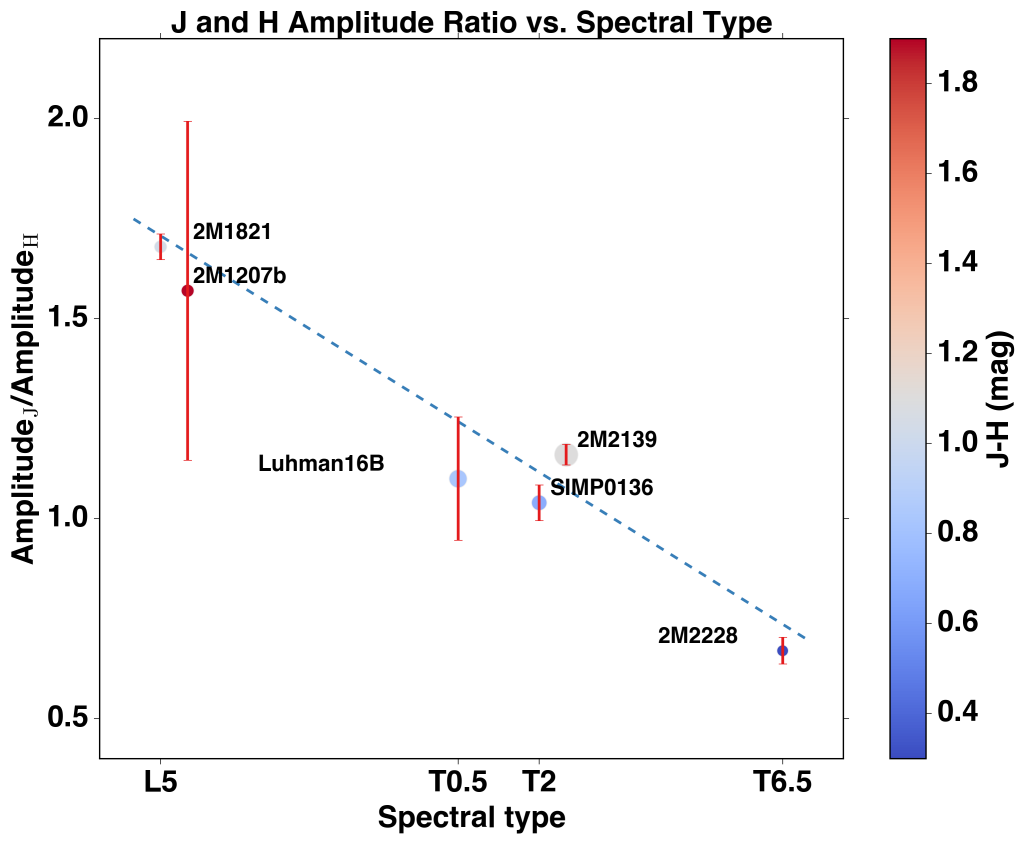
Rotational modulations of brown dwarfs have recently provided powerful constraints on the properties of ultra-cool atmospheres, including longitudinal and vertical cloud structures and cloud evolution. Furthermore, periodic light curves directly probe the rotational periods of ultra-cool objects. We present here, for the first time, time-resolved high-precision photometric measurements of a planetary-mass companion, 2M1207b. We observed the binary system with Hubble Space Telescope/Wide Field Camera 3 in two bands and with two spacecraft roll angles. Using point-spread function-based photometry, we reach a nearly photon-noise limited accuracy for both the primary and the secondary. While the primary is consistent with a flat light curve, the secondary shows modulations that are clearly detected in the combined light curve as well as in different subsets of the data. The amplitudes are 1.36% in the F125W and 0.78% in the F160W filters, respectively. By fitting sine waves to the light curves, we find a consistent period of 10.7 hr and similar phases in both bands. The J- and H-band amplitude ratio of 2M1207b is very similar to a field brown dwarf that has the identical spectral type but different J-H color. Importantly, our study also measures, for the first time, the rotation period for a directly imaged extra-solar planetary-mass companion.